Most adults require about 1.5 to 2 hours of deep sleep per night, which should make up roughly 20-25% of your total sleep.
This deep sleep window is essential for physical and mental recovery, and falling short of it can lead to cognitive issues, fatigue, and a weakened immune system.
-
Factors Influencing Deep Sleep:
-
Age: Deep sleep tends to decrease as you get older.
-
Lifestyle: Physical activity, diet, and daily habits all affect sleep quality.
-
Stress Levels: High stress can lead to poor sleep quality and less time spent in deep sleep.
-
Sleep Environment: Factors like noise, temperature, and light levels in your bedroom can disrupt sleep cycles.
-
Overall Health: Sleep disorders, chronic illness, or even inconsistent sleep schedules can negatively impact deep sleep.
Quick Tips to Improve Deep Sleep
-
Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock. A regular sleep schedule makes it easier to transition into deep sleep because your body knows when it’s time to rest. Irregular schedules can confuse your circadian rhythm, leading to fragmented sleep. -
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Wind down before bed with calming activities like reading, meditating, or taking a warm bath. This routine signals to your brain that it’s time to relax and prepare for sleep. Avoid stimulating activities such as intense exercise or screen time, as they can keep you alert and delay the onset of deep sleep. -
Optimize Your Sleep Environment (Dark, Cool, and Quiet Room)
A comfortable sleep setting promotes better sleep quality. A dark, cool room (around 60-67°F or 15-20°C) helps your body lower its core temperature, which is necessary for falling into deep sleep. Noise machines or earplugs can help if you're in a noisy environment, and blackout curtains can block disruptive light. -
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake, Especially in the Evening
Caffeine is a stimulant that can block sleep-inducing chemicals in your brain, making it harder to fall asleep. Even if you think you can sleep after drinking caffeine, it can still reduce the time spent in deep sleep. Alcohol might make you feel drowsy, but it disrupts your sleep cycles later in the night, reducing deep sleep. -
Incorporate Regular Physical Activity Into Your Day
Exercise helps you fall asleep faster and improves overall sleep quality, particularly deep sleep. However, vigorous exercise right before bed can be counterproductive, as it raises your adrenaline and body temperature. Try to get physical activity earlier in the day or at least a few hours before bed. -
Manage Stress Through Relaxation Techniques
Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which interferes with your body’s ability to relax and enter deep sleep. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness meditation can reduce stress and make it easier to achieve restorative deep sleep. -
Consider Using a Sleep Tracker to Monitor and Improve Sleep Quality
Devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, or dedicated sleep monitors can give you insight into your sleep patterns, including how much time you spend in deep sleep. By tracking your sleep, you can identify what’s affecting your sleep quality and make adjustments to improve it over time.
Introduction: The Role of Deep Sleep in Health
Deep sleep is a vital stage of the sleep cycle where your body and brain perform essential recovery functions. Not only does sleep quantity matter, but sleep quality—and especially the amount of deep sleep—plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health.
Deep sleep is essential for physical recovery, brain function, and emotional well-being, making it one of the most critical phases of your nightly rest.
What is Deep Sleep?

Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), is the most restorative sleep stage. It occurs in the third stage of Non-REM (NREM) sleep and is characterized by slow brain waves called delta waves.
During this phase, your body performs key tasks such as tissue repair, muscle growth, and immune system strengthening. Unlike REM sleep, which is associated with dreams, deep sleep focuses on physical restoration.
The Sleep Cycle: Where Does Deep Sleep Fit In?
The sleep cycle has multiple stages, alternating between NREM and REM sleep. Deep sleep (Stage 3 NREM) occurs earlier in the night and tends to decrease as the night goes on.
In contrast, REM sleep increases in duration toward the end of the night. The first few sleep cycles contain the highest amount of deep sleep, which is why going to bed at a consistent time and getting a full night of rest is important.
Why is Deep Sleep Important?
Deep sleep is crucial for:
-
Tissue Repair and Growth: Your body regenerates cells, repairs muscles, and heals injuries.
-
Immune System Strengthening: During deep sleep, your immune system is boosted, helping you fight off illness.
-
Memory and Learning: Deep sleep plays a vital role in consolidating and storing memories, aiding in learning and brain development. In short, deep sleep helps rejuvenate both your physical and mental health, making it essential for overall well-being.
How Much Deep Sleep Do You Need?
Most adults require 1.5 to 2 hours of deep sleep per night, which typically makes up 20-25% of their total sleep. This requirement can vary based on factors like age, health, and activity level. Children and teenagers often need more deep sleep due to growth and development, while deep sleep decreases as you age.
How to Measure Deep Sleep
You can measure deep sleep with wearable devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, or sleep monitors that track your sleep stages. Some devices sync with apps that break down your sleep cycle and offer insights into the amount of deep sleep you’re getting. Sleep studies conducted in medical labs can also provide in-depth measurements if you suspect a sleep disorder.
What Can Impact Your Deep Sleep?
Several lifestyle and environmental factors can influence deep sleep:
-
Stress: Elevated stress levels interfere with your body’s ability to relax and enter deep sleep.
-
Diet: Consuming too much sugar, caffeine, or alcohol can negatively impact sleep cycles.
-
Sleep Disorders: Conditions like sleep apnea or insomnia can reduce the amount of deep sleep you get.
The Role of Age and Lifestyle in Deep Sleep

As you age, your body naturally spends less time in deep sleep. However, making lifestyle adjustments such as staying active, eating a balanced diet, and following good sleep hygiene can help you maintain deep sleep as you grow older.
7 Ways To Improve Deep Sleep
-
Stick to a Regular Sleep Schedule
Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day. A consistent schedule helps regulate your circadian rhythm, making it easier to fall into deep sleep. -
Create a Calming Bedtime Routine
Engage in relaxing activities, like reading, meditation, or taking a bath, before bed to help your body wind down. -
Optimize Your Bedroom for Sleep
Keep your room cool, dark, and quiet. These conditions promote deeper sleep by creating an environment conducive to relaxation. -
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Avoid consuming caffeine or alcohol, especially in the evening, as they can disrupt your sleep cycles and reduce the amount of deep sleep you get. -
Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity increases the likelihood of falling into deep sleep. Aim to exercise earlier in the day, as vigorous activity right before bed can keep you awake. -
Manage Stress
Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your day, such as yoga or mindfulness exercises, to help reduce cortisol levels that interfere with deep sleep. -
Use a Sleep Tracker
Devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers can help monitor your sleep patterns and identify areas for improvement in your deep sleep cycle.
Myths and Facts About Deep Sleep
Myth: "More deep sleep is always better."
Fact: Deep sleep is important, but you need a balance of all sleep stages, including light sleep and REM sleep, to feel fully rested and restored.
Key Takeaways
Deep sleep is essential for overall health and plays a significant role in physical recovery, brain health, and immune function. Focus on improving your sleep quality, and incorporate habits that encourage more deep sleep to feel well-rested and energized each day.
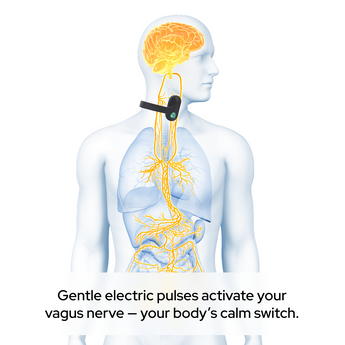
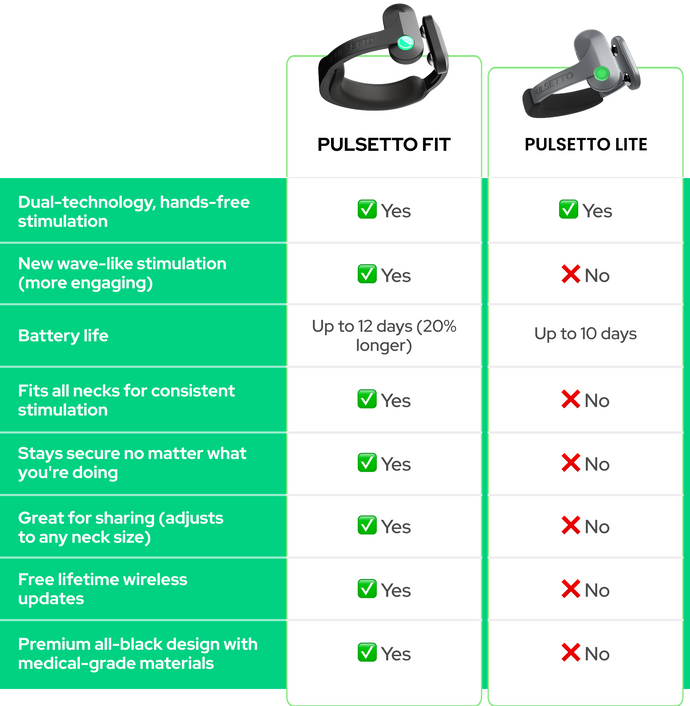
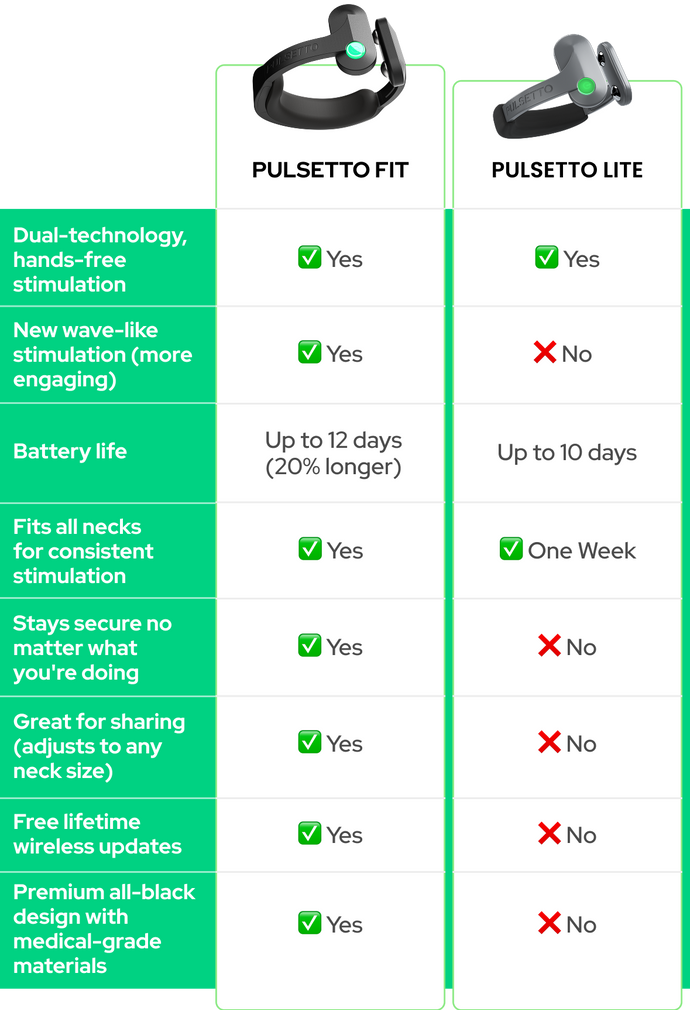
Pulsetto: The Ultimate Solution for Deep Sleep

If you’re looking for a simple way to improve your deep sleep, Pulsetto can be the ultimate solution. Pulsetto uses vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) to help calm your nervous system, reduce stress, and promote relaxation—all crucial for getting more deep sleep.
By integrating with wearable devices, Pulsetto allows you to monitor your sleep patterns, providing actionable insights to improve your overall sleep quality.
With its unique technology, Pulsetto makes it easier for you to achieve restful, restorative deep sleep so you can wake up feeling refreshed and energized every day.